Law
Understanding the Basics: Magnuson-Moss Warranty Act for Dummies

Are you aware of the Magnuson-Moss Warranty Act and how it impacts your consumer rights? This federal warranty law, often overlooked, is crucial for anyone making a purchase in the United States.
It governs warranties on consumer products, providing valuable safeguards. Understanding this act is essential for making informed decisions and protecting your investments. Sounds complicated?
Fear not, we’re here to break it down into simple terms. This guide on the Magnuson-Moss Warranty Act for dummies will help you grasp the key points without the legal jargon and complexities.
Ready to learn more? Let’s begin!
What is the Magnuson-Moss Warranty Act?
The Magnuson-Moss Warranty Act is a federal law passed in 1975. It regulates warranties on consumer products sold in the United States.
This act aims to protect consumers by ensuring they have enough information about warranties before purchasing. It applies to any product that costs more than $15 and comes with a warranty.
This includes products such as:
- cars
- appliances
- electronics
- software
It requires manufacturers to provide clear and detailed information about their warranties. It also prevents them from using deceptive or unfair practices that can mislead consumers.
Types of Warranties Covered
There are two main types of warranties covered by the Magnuson-Moss Warranty Act. Knowing the difference between these warranties is key to protecting your consumer rights.
The two main types of warranties are:
Full Warranty
A full warranty means the manufacturer must repair or replace a defective product at no cost to the consumer. It must also ensure the product can be fixed within a reasonable time.
The consumer must be given a new product or a full refund if it cannot be repaired.
Limited Warranty
A limited warranty may cover only certain parts or specific types of defects. The manufacturer might require the consumer to pay for part of the repair or replacement costs.
However, it can impose restrictions on the duration of implied warranties. So it is important to read and understand the terms before making a purchase.
How to Use Your Warranty Rights
To use your warranty rights, start by reading the warranty terms carefully. Keep a copy of your purchase receipt and any warranty documentation.
If a product defect arises, notify the manufacturer or retailer immediately. Document the issue with photos or written descriptions.
If your warranty claims are not addressed, you can seek help through agencies or consult legal help from a reputable advocate.
For instance, you might consider seeking assistance from professionals, like Hawaii Lemon Law attorneys, who specialize in such matters. They can provide expert guidance to ensure your claims are properly handled.
Remedies for Breach of Product Guarantees
When a manufacturer or seller fails to honor the terms of a warranty, it is known as a breach of warranty. There are several remedies available to consumers such as:
- repair or replacement
- refund
- compensation for damages
- legal action
For smaller amounts, you can file a claim in small claims court. This type of court handles minor disputes without the need for an attorney. It is a quicker and less costly way to resolve warranty issues.
The Basics of Magnuson-Moss Warranty Act for Dummies
Understanding your rights is crucial for protecting your investments. This Magnuson-Moss Warranty Act for dummies is created to empower you as a consumer. So make sure you read and understand warranties before you buy.
Don’t hesitate to seek help if you face issues. Stay informed and make your purchases with confidence!
Did you find this article helpful? Check out the rest of our blog now!
Law
Chealse Sophia Howell Files Lawsuit Against Grant Cardone and Cardone Capital Highlighting Digital Business Accountability
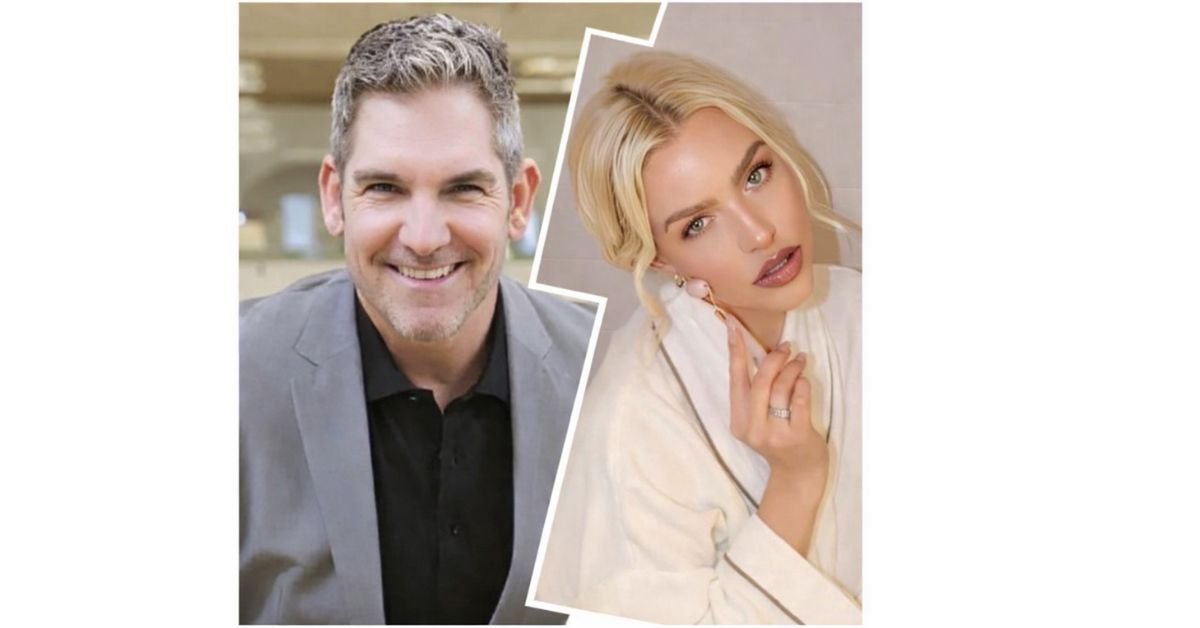

MIAMI, FL — Chealse Sophia Howell, a former Miss Universe Canada delegate and entrepreneur, has filed a civil lawsuit in Miami-Dade County, Florida, against sales trainer and real estate investor Grant Cardone and his company, Cardone Capital, LLC. The lawsuit raises broader questions about accountability, influence, and responsibility in the digital business environment, particularly regarding statements made on widely followed social media platforms.
According to the complaint, Howell alleges that Grant Cardone used his social media presence to publish and amplify statements implying her involvement in serious criminal activity, including accusations she denies. The lawsuit contends that these statements reached millions of users across platforms such as Instagram, X, Facebook, and LinkedIn, significantly amplifying their impact and causing tangible harm to Howell’s personal and professional life.
Howell’s filing emphasizes the increasing risks for business leaders who rely on digital platforms for communication and branding. The complaint asserts that statements made by influential figures can have immediate and far-reaching consequences, including reputational damage, lost business opportunities, financial losses, and concerns for personal safety. According to court documents, the scale and permanence of social media amplify the potential harm from false or misleading statements, creating challenges for individuals and companies operating in highly visible industries.
The lawsuit outlines multiple causes of action, including defamation per se, defamation by implication, and tortious interference with contractual and advantageous business relationships. Howell alleges that Grant Cardone and Cardone Capital acted with actual malice, meaning that the statements were published with knowledge of their falsity or with reckless disregard for whether they were true. These claims reflect the complex legal questions that arise when online speech intersects with professional and business interests.
According to court filings, Howell is the founder of Haute Agency, a talent management and brand development firm representing models, influencers, and creatives, and also operates a skincare company under her name. The complaint asserts that her professional success depends heavily on credibility, trust, and long-term relationships with clients, partners, and sponsors. The alleged defamatory statements, Howell claims, disrupted business relationships, led to canceled endorsements, and caused prospective partnerships to be abandoned.
The lawsuit further alleges that the posts created real-world consequences, including harassment and threats. The complaint states that online users sought information about Howell’s personal whereabouts, creating safety concerns and emotional distress. Howell’s legal team emphasizes that these outcomes illustrate how statements by individuals with substantial online influence can extend far beyond mere commentary and into areas with serious practical implications.
In addition to compensatory damages, Howell seeks injunctive relief to prevent Grant Cardone and Cardone Capital from continuing to disseminate or amplify the alleged statements. The filing argues that monetary damages alone are insufficient to address the ongoing harm caused by the persistence of these statements online, which can continue to affect public perception and business relationships long after their initial publication. Howell also seeks recovery of attorneys’ fees and costs and has demanded a jury trial. Punitive damages may also be pursued, reflecting claims of intentional and malicious conduct.
Legal observers note that cases involving alleged online defamation are becoming increasingly significant as courts consider how traditional legal standards apply to modern digital communication. Lawsuits such as Howell’s may influence how business leaders approach public statements, particularly when those statements have the potential to damage reputations and disrupt professional relationships. Experts suggest that the outcomes of such cases could inform broader standards of accountability and responsibility for individuals with substantial social media followings.
The filing against Grant Cardone and Cardone Capital also highlights broader issues related to digital influence and public perception. According to the complaint, the rapid dissemination and visibility of online statements mean that reputational harm can occur almost immediately and persist indefinitely through reposts, search engine indexing, and commentary. Courts may increasingly be called upon to balance protections for free speech with remedies for individuals and businesses harmed by online statements.
Howell’s lawsuit remains pending in Miami-Dade County Circuit Court. No rulings have been issued, and all claims described in the filing remain allegations. Grant Cardone and Cardone Capital have not been adjudicated responsible for the claims at this time. The case is being closely watched by legal observers and business leaders alike due to its potential implications for how online influence, speech, and accountability are evaluated in the digital business landscape.
Also Check:
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1Uyk_ZHhL84JKT_v2_UdsSYS_XgD7TR-t/view?usp=drivesdk
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1crUZMoULb3sVNaSAXn_amXsl_B_bMFO0/view?usp=drivesdk
Disclaimer: This article summarizes allegations contained in a civil complaint. All defendants are presumed innocent unless and until proven otherwise in a court of law.
Law
Understanding Different Types of Catastrophic Injury Cases

When the word “catastrophic injury” comes up, it usually makes us think of terrible accidents that change lives forever. But what exactly is a catastrophic injury?
These injuries are very severe and often require long-term medical care. They can arise from various situations, and understanding them is important for multiple reasons.
Understanding catastrophic injuries helps us be more prepared and know how they affect us and our loved ones.
What Is a Catastrophic Injury?
A catastrophic injury is a type of injury that has serious, long-lasting effects. People with these injuries can have difficulty doing everyday tasks.
For example, they might struggle with walking, talking, or taking care of themselves. Some injuries can result in permanent disabilities, requiring constant assistance and costly care. There are many types of catastrophic injuries. Below are some common examples:
- Brain Injuries
- Spinal Cord Injuries
- Amputations
- Severe Burns:
- Multiple Fractures
Common Causes of Catastrophic Injuries
Understanding the causes of these injuries helps us know how to avoid them. Here are some common causes of catastrophic injuries:
Motor Vehicle Accidents
Car accidents are one of the leading causes of catastrophic injuries. Every year, thousands of people are hurt or killed in crashes. Some drivers might be reckless, distracted, or even under the influence of alcohol. Always wearing seat belts and following traffic rules can help keep us safer on the road.
Workplace Accidents
Many people work in jobs that can be dangerous, leading to serious injuries. Construction sites, factories, and entertainment venues can have safety risks. Proper training and equipment might prevent these injuries and save lives.
Sports and Recreation
While sports are fun and healthy, they can also lead to injuries. Contact sports like football or hockey can cause concussions or other severe injuries. Using safety gear, like helmets and pads, can help protect players.
Violent Crimes
Sadly, some people experience catastrophic injuries due to violence. This might happen during fights or attacks. Communities need to work together to prevent violence and keep each other safe.
The Impact of Catastrophic Injuries
Living with a catastrophic injury affects not just the injured person but their families as well. Here are some ways these injuries can impact lives:
Physical Effects
People with catastrophic injuries often face ongoing physical challenges, need regular treatment. This can include surgeries, therapy, and medications to manage pain.
Emotional and Psychological Effects
Not only do catastrophic injuries change physical abilities, but they can also impact emotions. Injured individuals may experience depression, anxiety, or frustration related to the loss of independence.
Financial Burdens
The costs of medical care for catastrophic injuries can be huge. In some cases, families may find they need to adjust their lifestyles to afford necessary treatments. Legal support may be needed to help recover costs.
Understanding Your Rights
If you or a loved one experiences a catastrophic injury, it is essential to know your rights. Seeking compensation for medical bills and suffering is vital. A catastrophic injury lawyer can help you navigate the legal process. They can explain your case and advocate on your behalf to ensure you receive fair compensation.
Taking Action
Catastrophic injuries are serious matters that can affect anyone. By understanding what causes these injuries and their potential impacts, we can work together to prevent them.
If you or someone you know is injured, consider seeking help from a catastrophic injury lawyer who can guide you through recovery and help protect your rights. Remember, being informed is one of the best ways to ensure safety for ourselves and our loved ones.
Catastrophic injuries, such as traumatic brain injuries, spinal cord damage, or severe burns, can permanently alter a person’s life. In these situations, working with an experienced catastrophic injury lawyer is critical. They understand the long-term impact of such injuries and can help you pursue the full compensation needed for medical care, lost income, and future support.
Law
How Back Injury Claims Really Work in Austin

Austin sees its fair share of traffic and chaos, and when that chaos leads to injury, the aftermath can be painful in more ways than one. A back injury from a car accident is not always visible, but the pain, medical visits, and stress of missing work are real. These injuries disrupt lives, and trying to manage legal claims on top of recovery only adds to the pressure.
That is where the right help matters. Working with a compensation lawyer for back injuries from car accidents allows you to focus on healing while someone else takes on the fight. A qualified attorney knows how to pursue fair compensation while protecting your long-term financial future.
A spinal cord injury can have life-changing consequences, affecting everything from mobility to independence. In such serious cases, it’s essential to have a skilled spinal cord injury lawyer on your side who understands the medical and legal complexities involved. They can fight for the compensation you need for long-term care, rehabilitation, and future expenses.
What Makes a Back Injury Claim Legitimate?
Every claim needs proof. You need to show that another party was at fault and that the injury resulted in real damages. That includes medical bills, lost income, and changes to your ability to live and work the way you did before the accident. It also consists of the physical and emotional impact of the injury itself.
Medical documentation is a significant part of the process. This means doctor visits, imaging tests, therapy records, and follow-up care are all needed to support your claim. Spinal injuries can have a wide range of long-term effects on physical function and daily life.
What Goes Into Calculating Damages?
Compensation involves more than paying medical bills. Economic damages cover direct costs—surgeries, medications, physical therapy, and lost income from missed work. Non-economic damages, on the other hand, account for pain, suffering, emotional distress, and how your injury changes your everyday life.
For many people, a back injury means giving up things they once did easily. That includes lifting a child, doing a job they love, or sleeping without pain. Attorneys gather details from your doctors and your personal experiences to make sure your whole situation is represented in the claim.
Why does Legal Support matter so Much?
Insurance companies are not on your side. Their goal is to settle quickly and minimize their expenses. Without an attorney, it becomes harder to push back. An experienced back injury attorney understands the long-term complications these injuries can bring. They know how to negotiate with insurers, bring in medical experts, and calculate fair settlements that reflect both current and future costs.
There is also the legal side to manage—filing deadlines, paperwork, legal strategy, and potential court appearances. In Texas, waiting too long to file can disqualify you from receiving any compensation. A knowledgeable attorney keeps everything on track and ensures that your rights are protected.
What does the Process Usually look like?
Most cases follow a standard process:
- Review of evidence and documentation
- A demand letter sent to the insurance company
- Negotiation for a fair settlement
- Filing a lawsuit if necessary
- Discovery and depositions
- Final settlement or trial
The process can take time, and that is where patience and proper guidance are most crucial.
Final Thoughts
Back injuries often become worse with time. Even a mild injury can lead to long-term pain and nerve issues. That is why the outcome of your claim should not be based only on what you are experiencing today.
Working with the right attorney helps protect your future. With someone fighting for what you need, you can concentrate on recovery without losing control of your financial well-being.
-

 Entertainment8 months ago
Entertainment8 months agoExplore The Kristen Archives: A Treasure Trove Of Stories & More
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoWhat is O Farming: How to Make Money Online and Its Start-Up Benefits
-

 Law9 months ago
Law9 months agoProtect Your Vehicle with These Smart Motor Insurance Strategies
-

 Entertainment2 years ago
Entertainment2 years agoSandra Orlow: Exploring the Life and Legacy of a Cultural Icon
-
 General1 year ago
General1 year agoBaby Alien Fan Bus: Watch Parts 2 & 3 on Twitter, Reddit!
-

 Technology2 years ago
Technology2 years agoGeekzilla Radio: Your Portal to the Ultimate Geeky Adventure!
-

 General1 year ago
General1 year agoDiana Nyad & Bart Springtime: A Swim to Success
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoTex9.Net Crypto: Fast, Secure International Money Transfers with Competitive Rates
