Pets
Uncovering the Mysteries of the Magnificent Palomino Horse Breed
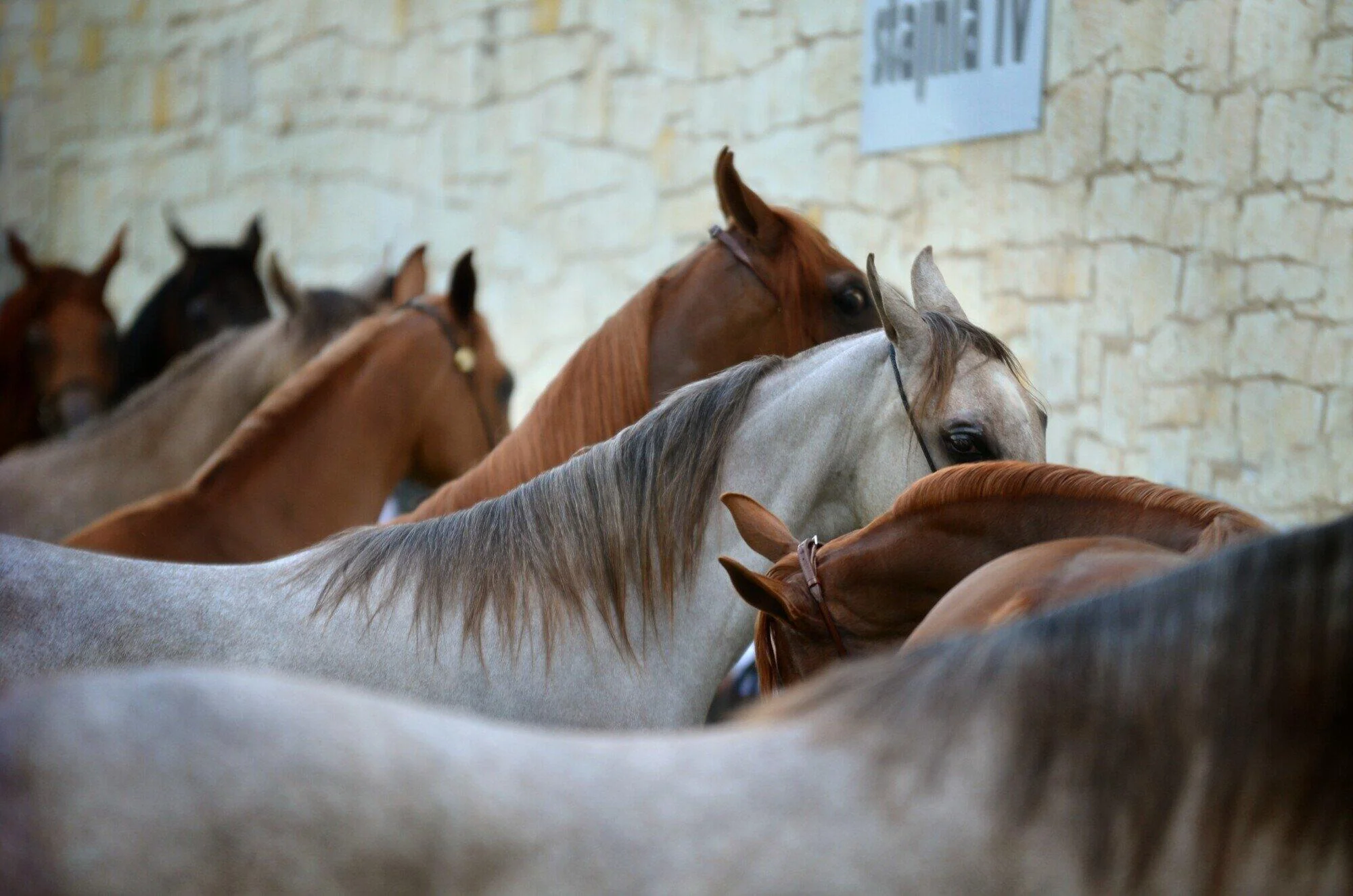

The equestrian world is filled with awe-inspiring horse breeds. However, few are as captivating as the palomino.
Known for their distinctive golden coats and striking appearance, palomino horses have a rich history. They hold a unique place in the hearts of horse lovers.
If you’re curious continue reading. In this article, we’ll explore the fascinating aspects of the palomino horse breed. We’ll shed light on what makes them so special.
Let’s begin!
The Golden Beauty
The first thing that catches your eye about a palomino horse is its stunning coat. The golden hue can range from a deep, rich gold to a light, almost cream color.
This beautiful coat is complemented by a white or light cream mane and tail. It gives the palomino a striking contrast that makes them stand out in any stable.
The unique coloring is due to a genetic trait known as the cream gene, which dilutes the base coat color. This gene is what gives the palomino horse its signature look. This makes it one of the most visually appealing horse breeds.
A Breed of Many Breeds
Contrary to popular belief, the palomino is not a specific breed but rather a color classification. This means that palomino horses can be found within many different breeds. This includes the American Quarter Horse, the Arabian, and the Thoroughbred.
The defining feature is the golden coat color. This can appear in any breed that carries the cream gene.
The diversity adds to the allure of the palomino. You can find beautiful palomino horses across various breeds, each with their own unique characteristics.
Rich History
The history of the palomino horse is as rich as its coat color. The name “palomino” is believed to have Spanish origins, named after a golden grape variety.
Palomino horses were highly prized by royalty and nobility throughout history. They were often seen as symbols of wealth and prestige.
The Spanish conquistadors are credited with bringing palomino horses to the Americas, where they quickly became cherished by Native American tribes and early settlers. This historical palomino horse origin has cemented the breed’s place in the annals of equestrian lore.
Palomino in Popular Culture
Horse palominos have not only captured the hearts of equestrians. They have also made a significant impact on popular culture.
One of the most famous palominos was Trigger, the beloved horse of cowboy actor Roy Rogers. Trigger’s intelligence and beauty made him a star in his own right. He has appeared in numerous films and television shows.
He is proof that the palomino’s striking appearance has made it a favorite in the media. They often symbolize heroism and nobility. Their presence in popular culture has only added to the mystique and allure of the breed.
Versatile Performers
Palomino horses are not just pretty faces. They are also highly versatile and capable performers. Depending on the breed, palominos can excel in various disciplines. This includes dressage, show jumping, western pleasure, and trail riding.
Their striking appearance often gives them an edge in the show ring. They catch the judges’ eyes right away.
Beyond competition, palominos are known for their friendly and willing temperaments. This makes them excellent companions for riders of all levels.
The combination of beauty and versatility makes the palomino a popular choice among equestrians. They truly are a golden treasure in the world of horses.
The Care and Maintenance
Maintaining a palomino’s golden coat can require a bit of extra care, but the results are well worth it. Regular grooming is essential to keep their coats shiny and healthy. This includes frequent brushing to remove dirt and debris that can dull the coat’s luster.
Bathing with specialized shampoos can enhance the coat’s natural color. You’ll need to find a shampoo that is safe for their sensitive skin.
You also need to keep palomino horses out of direct sunlight can help prevent the fading of their coats. Providing shade or using fly sheets and masks can protect them from harmful UV rays.
Additionally, a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients will help maintain the coat’s vibrant hue. Proper care ensures that the palomino always looks its best, showcasing its magnificent coloring.
Genetic Intricacies
As previously mentioned, the palomino coat color is due to the cream gene. This gene has a 50/50 chance of being passed down from one generation to another.
This means that not every foal produced by two palomino parents will be a palomino. There is also a possibility of producing a chestnut or cremello foal, depending on the genetics inherited from the parents.
Understanding these genetic intricacies is essential for breeders and owners of palomino horses. This is because it can influence breeding decisions and expectations for coat color.
Health Considerations
Just like any other horse breed, palominos are susceptible to certain health conditions. One common concern is photosensitivity. This is a condition that makes their skin sensitive to sunlight and can result in sunburns or even skin cancer.
Regular veterinary check-ups and proper care can help prevent and manage these health issues. This includes providing adequate shade, applying sunscreen, and using fly masks and sheets.
Building a Bond
Lastly, owning a palomino horse is not just about admiring its beauty and performance. It’s also about building a bond with these majestic creatures. They have an incredible ability to connect with their owners and become loyal companions.
The relationship between rider and horse is one of trust, respect, and communication. It can be an incredibly fulfilling experience.
Palomino Associations and Registries
There are various associations and registries dedicated to the palomino horse. These organizations promote and preserve the breed. At the same time, they recognize exceptional horses through shows, competitions, and awards.
Some notable associations include the Palomino Horse Breeders of America (PHBA) and the American Palomino Horse Association (APHA). These organizations provide resources for owners, breeders, and enthusiasts. They allow them to connect and share their love for the palomino horse.
The Palomino Horse Breed Is Special
The palomino horse breed captivates us with its striking appearance and rich history. Its versatility, intelligence, and loyalty make it a favorite among equestrians and in popular culture.
But beyond the surface level, palominos embody everything that makes horses so special – strength, grace, and an indescribable connection with humans. They are truly one of a kind. So next time you see a golden beauty, take a moment to appreciate and celebrate all the qualities that make them such an iconic breed in the equestrian world.
Was this article helpful? Then check out the rest of our site for more.
Pets
Dog Vomiting & Shaking: Signs Of Physical Imbalance

When your dog is vomiting and shaking, it can be a concerning and stressful situation for pet owners. These symptoms often indicate an underlying physical imbalance or health issue that requires prompt attention.
In this article, we will explore the common causes of dog vomiting and shaking, the importance of seeking veterinary care, and steps you can take to help your furry friend during this time.
TRENDING
Exploring The Benifits Of Buying Freehold Real Estate
Understanding The Causes Of Dog Vomiting And Shaking
There are several potential causes for a dog to experience vomiting and shaking simultaneously. Some of the most common reasons include:
Gastrointestinal Issues
Gastrointestinal (GI) problems such as gastroenteritis, pancreatitis, or inflammatory bowel disease can lead to vomiting and shaking in dogs. These conditions can be caused by dietary indiscretions, infections, or underlying medical conditions.
Toxin Ingestion
Ingesting toxic substances, such as certain foods, plants, or chemicals, can cause severe gastrointestinal distress and neurological symptoms like shaking. Some common toxins include chocolate, xylitol, antifreeze, and certain household cleaners.
Pain Or Discomfort
Conditions that cause pain or discomfort, such as arthritis, dental problems, or injuries, can trigger vomiting and shaking in dogs. The shaking may be a response to the pain or discomfort.
Metabolic Disorders
Metabolic disorders, such as diabetes, kidney disease, or liver disease, can lead to vomiting and shaking. These conditions can cause an imbalance in the body’s systems, leading to various symptoms.
Neurological Issues
Neurological problems, such as seizures or vestibular disease, can cause vomiting and shaking. These conditions can be caused by underlying medical conditions or injuries to the brain or inner ear.
Seeking Veterinary Care
If your dog is vomiting and shaking, it is crucial to seek veterinary care as soon as possible. These symptoms can quickly lead to dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and other serious health issues if left untreated.
During your visit, your veterinarian will perform a physical examination and may recommend diagnostic tests, such as blood work, urinalysis, or imaging studies, to determine the underlying cause of your dog’s symptoms. Treatment will depend on the specific diagnosis but may include fluid therapy, medication, dietary changes, or surgery in some cases.
Providing First Aid At Home
While waiting to see your veterinarian, there are some steps you can take to help your dog and provide first aid at home:
- Withhold Food And Water: If your dog is vomiting, it is best to withhold food and water for at least a few hours to allow their stomach to settle. Provide small amounts of water every few hours to prevent dehydration.
- Keep Your Dog Calm And Comfortable: Provide a quiet, comfortable place for your dog to rest and avoid stressful situations. You can also use a warm compress on their abdomen to help relieve any discomfort.
- Monitor For Signs Of Dehydration: Check for signs of dehydration, such as sunken eyes, dry gums, or decreased skin elasticity. If you notice these signs, contact your veterinarian immediately.
- Avoid Giving Medications: Do not give your dog any medications, including over-the-counter medications, without consulting your veterinarian first. Some medications can be harmful to dogs and may interact with any underlying conditions.
Preventing Future Episodes
Once your dog has recovered from their vomiting and shaking episode, there are steps you can take to help prevent future occurrences:
- Provide a Balanced Diet: Feed your dog a high-quality, balanced diet that is appropriate for their age, size, and activity level. Avoid feeding table scraps or human foods, as these can cause gastrointestinal issues.
- Secure Toxic Substances: Keep all toxic substances, such as chemicals, medications, and certain foods, out of your dog’s reach. Store them in a secure location and always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for use and disposal.
- Maintain a Clean Environment: Keep your dog’s living space clean and free of potential hazards, such as sharp objects or small items that could be swallowed. Regular cleaning and grooming can also help prevent the spread of infections.
- Provide Regular Veterinary Care: Schedule regular check-ups with your veterinarian to ensure your dog’s overall health and well-being. This can help catch any potential issues early and prevent more serious problems from developing.
Conclusion
Dog vomiting and shaking can be concerning symptoms that indicate an underlying physical imbalance or health issue. By understanding the potential causes, seeking prompt veterinary care, and taking steps to prevent future episodes, you can help keep your furry friend happy and healthy.
Remember, your veterinarian is your best resource for ensuring your dog’s well-being, so don’t hesitate to reach out if you have any concerns.
ALSO READ: Salad Fork
FAQs:
What should I do if my dog is vomiting and shaking?
If your dog is vomiting and shaking, it is important to seek veterinary care as soon as possible. In the meantime, withhold food and water, keep your dog calm and comfortable, monitor for signs of dehydration, and avoid giving any medications without consulting your veterinarian first.
Can vomiting and shaking be life-threatening for dogs?
Yes, vomiting and shaking can be life-threatening if left untreated. These symptoms can quickly lead to dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and other serious health issues. Seeking prompt veterinary care is crucial.
What are some common causes of vomiting and shaking in dogs?
Some common causes of vomiting and shaking in dogs include gastrointestinal issues, toxin ingestion, pain or discomfort, metabolic disorders, and neurological problems. Your veterinarian will perform diagnostic tests to determine the underlying cause.
How can I prevent future episodes of vomiting and shaking in my dog?
To prevent future episodes of vomiting and shaking, provide a balanced diet, secure toxic substances, maintain a clean environment, and schedule regular veterinary check-ups. Avoid feeding table scraps or human foods and keep your dog’s living space free of potential hazards.
When should I take my dog to the vet for vomiting and shaking?
If your dog is vomiting and shaking, it is best to seek veterinary care as soon as possible. These symptoms can quickly lead to serious health issues if left untreated. Contact your veterinarian immediately if your dog is showing signs of dehydration or if the vomiting and shaking persist for more than a few hours.
Pets
Exploring the Top 4 Things to Consider Before Purchasing a K9 Puppy
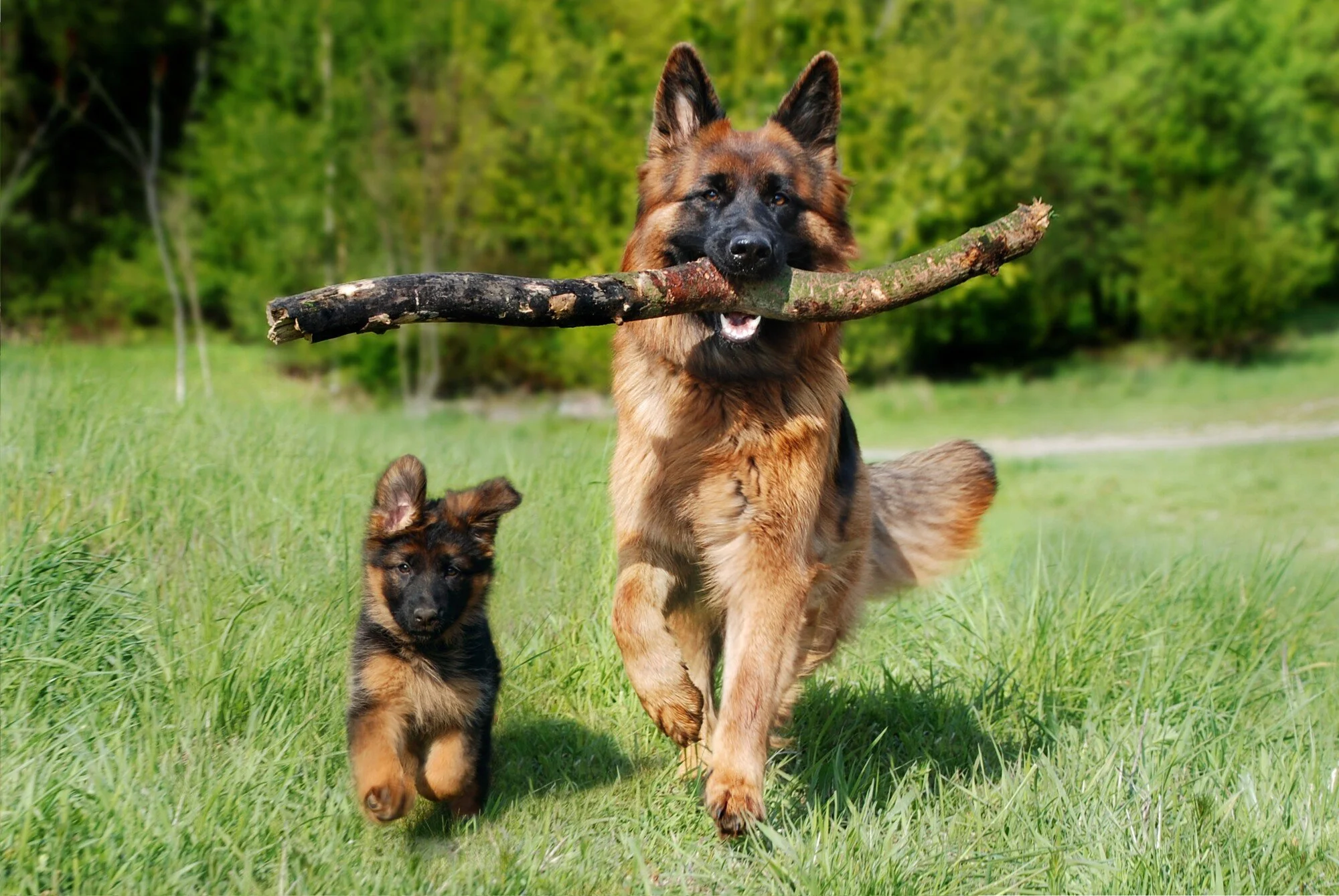

Purchasing a K9 puppy can be an exciting and life-changing decision. These intelligent and loyal creatures make great companions, whether you are looking for a new addition to your family or a working partner.
However, owning a K9 puppy comes with many responsibilities and requires careful consideration before making the purchase.
In this guide, we will explore the top 4 things you should consider before purchasing a K9 puppy.
1. Breed Suitability and Purpose
Before purchasing a K9 puppy, it is essential to research the different breeds available and determine which one best suits your lifestyle and purpose.
Intended Use
Determine why you want a K9 puppy. Different breeds excel in various roles such as police work, search and rescue, protection, or as family pets. When looking at Guard Dogs For Sale, ensure the breed matches your intended purpose, whether it’s for protection or companionship.
Temperament and Training
Different dog breeds have different temperaments, energy levels, and how easy they are to train. Some breeds need more exercise and mental challenges than others. When choosing a breed, it’s important to think about these factors to make sure you can give the right environment and training for your puppy.
Physical Requirements
Some breeds may have specific physical requirements, such as grooming needs or exercise demands. It is crucial to consider these factors and determine if you can meet them before purchasing a K9 puppy.
2. Lifestyle Compatibility
Owning a K9 puppy can significantly impact your lifestyle. Before making the purchase, it is important to consider how a new four-legged family member will fit into your daily routine.
Time Commitment
K9 puppies require time and attention for training, exercise, and companionship. It is essential to evaluate your schedule and make sure you can devote enough time to your K9 puppy’s needs.
Living Environment
Different dog breeds have different needs. Some are fine in apartments, while others need space to run and play. Think about your home and if it suits the breed you like.
Financial Considerations
Owning a puppy costs money for food, vet visits, and training. Check if you can afford these expenses before getting a puppy.
3. Health and Genetics
The health and genetics of a K9 puppy should also be carefully considered before making a purchase. Here are some things you should consider:
Breeder Reputation
It’s important to buy from a reputable breeder who cares about their puppies’ health. Check the breeder’s reputation, read reviews, and ask for references before buying.
Genetic Health Testing
A responsible breeder tests their dogs for genetic health to ensure they don’t pass on any hereditary diseases to their puppies.
Medical History
Ask the breeder for the puppy’s medical history. It’s important to know your new puppy’s health before bringing them home.
4. Time and Patience for Training
Training a K9 puppy takes time, patience, and consistency. It is crucial to have realistic expectations about the training process and be prepared to invest the necessary time and effort. This is especially important for working or specialized breeds that require specific training.
Consider these Essentials Before Getting a K9 Puppy
Owning a K9 puppy is a big commitment and needs careful thought. Keep these four things in mind to make a smart choice when getting a K9 puppy that suits your life, needs, and likes.
Always research and talk with experts before deciding to make sure it’s best for you and your new furry friend. Take your time, do your research, and enjoy finding the perfect K9 puppy for you!
Is this article helpful? Keep reading our blog for more.
Pets
Maintaining a Healthy Environment for Small Saltwater Fish

Creating and maintaining a healthy environment for small saltwater fish can be both rewarding and challenging. Saltwater aquariums are known for their vibrant colors and diverse marine life, but they also require meticulous care and attention to ensure the well-being of your aquatic pets.
This guide will walk you through essential steps to keep your small saltwater fish happy and healthy.
Choosing the Right Aquarium
When choosing the right aquarium, size is an important factor to consider. Small fish need space to swim and explore. Look for an all-in-one saltwater aquarium that includes built-in filtration and lighting.
This can make setup much easier and ensure a balanced environment. It’s also crucial to select an aquarium made from high-quality glass or acrylic. Additionally, make sure the aquarium has a sturdy stand to support its weight.
Cycling the Aquarium
Cycling the aquarium is a critical step in preparing your salt reef tank for its new inhabitants. This process involves establishing beneficial bacteria that will break down harmful toxins, such as ammonia and nitrites, ensuring a safe environment for your fish.
Begin by adding a source of ammonia to the tank, which can come from fish food, pure ammonia, or other organic materials. Monitor the levels of ammonia, nitrites, and nitrates regularly using water testing kits.
Patience is key, as cycling can take several weeks to complete, but it is essential for the long-term health of your salt reef tank. Once the cycling process is complete, you can gradually introduce your small saltwater fish into their new, stable habitat.
Selecting Suitable Fish
When selecting suitable fish for your saltwater aquarium, it’s essential to choose species that can thrive in your tank’s environment. Make sure to research each fish’s needs regarding tank size, water conditions, and dietary requirements.
For newcomers, it’s often best to start with hardy fish that are easy to care for. For example, the Blue Hippo Tang is a popular choice due to its stunning appearance and ability to adapt to various tank setups. Always ensure that the fish you select are compatible with each other to avoid stress and aggression in your aquarium.
Monitoring Water Quality
Monitoring water quality is crucial for maintaining a healthy saltwater aquarium. It involves regularly checking parameters such as temperature, salinity, pH, ammonia, nitrites, and nitrates. Consistent water testing helps you detect any imbalances early, allowing prompt correction.
Use reliable test kits and record your results to track trends over time. Perform regular water changes to remove toxins and replenish essential minerals. Always condition tap water before adding it to your tank to eliminate chlorine and other harmful substances. Properly maintaining water quality ensures a stable and thriving environment for your small saltwater fish.
Feeding Your Fish
Feeding your fish is an important part of keeping them healthy and happy. Choose high-quality fish food that meets the dietary needs of your specific fish species. It’s best to feed small amounts of food two to three times a day. Overfeeding can lead to poor water quality and health problems for your fish.
Remove any uneaten food after a few minutes to prevent it from decaying in the tank. Incorporate a variety of foods, such as flakes, pellets, and frozen options, to provide balanced nutrition.
Occasionally, treat your fish with live or freeze-dried foods for added variety and stimulation. Consistently observe how much your fish eat to adjust feeding amounts as necessary.
Maintaining the Aquarium
Keeping the aquarium clean is very important for the health of your fish. Regular maintenance tasks are a must to ensure a healthy environment. Start by checking and cleaning the filters every week. They are essential for removing waste and keeping water clear.
Also, replace about 10-20% of the water with fresh saltwater each week. This helps remove any toxins that can build up. Clean the glass of your aquarium to prevent algae from growing. Use an algae scrubber or magnet cleaner to make it easy.
Don’t forget to check all equipment to ensure everything is working correctly. Regular maintenance will keep the aquarium looking beautiful and your fish happy.
Dealing with Common Issues
When dealing with common issues in a saltwater aquarium, it is crucial to stay vigilant and proactive. Look out for signs of fish stress, such as unusual swimming patterns or loss of appetite. Algae growth can become a problem, making the tank look dirty and affecting water quality.
To control algae, reduce the amount of light and clean the tank regularly. Another common issue is the presence of harmful parasites that can harm your fish. To prevent this, quarantine new fish before adding them to the tank.
Monitor water parameters closely to detect any sudden changes. Regularly testing water quality will help you catch issues early. Maintaining a clean and stable environment is key to avoiding common problems.
Enjoying Your Saltwater Aquarium
Creating and maintaining a healthy environment for small saltwater fish can be hard. However, it is also very rewarding. When you set up your aquarium, make sure to choose the right size for your fish. Small fish need space to swim and be happy.
Cycling the aquarium is very important before you add any fish. This process can take several weeks. It helps to make the water safe by building good bacteria. Checking the water quality regularly will keep your fish healthy.
Feeding them the right food and keeping the tank clean will also help. By doing these things, you can enjoy a vibrant and healthy saltwater aquarium.
Learn All About Small Saltwater Fish
Taking care of small saltwater fish isn’t easy, but it can be fun. You have to make sure their tank is the right size. Making the water safe with good bacteria is important before adding fish. Check the water often to keep the fish healthy.
Feed them the right food and keep their home clean. By doing these simple things, you can have a great saltwater aquarium. Enjoy watching your happy fish swim around in their colorful tank.
Did you find this article helpful? Check out the rest of our blog for more related content.

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoTex9.Net Crypto: Fast, Secure International Money Transfers with Competitive Rates

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoSandra Orlow: Exploring the Life and Legacy of a Cultural Icon

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoBaby Alien Fan Bus: Watch Parts 2 & 3 on Twitter, Reddit!

 General1 week ago
General1 week agoDiana Nyad & Bart Springtime: A Swim to Success

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoSnapchat Planets: Exploring Your Streak Universe

 General1 month ago
General1 month agoDeeper Dive into myfavouriteplaces. org:// blog

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoFintechZoom Apple Stock: Real-Time Insights and Expert Analysis

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoUnlock Your Fantasy: Dive into Coomer Party Free OnlyFans Leaks!