General
What Mentoring LTAP Is And How It Enhances Career Development

General
Inside The Forgeworld: Crafting Legends In Miniature
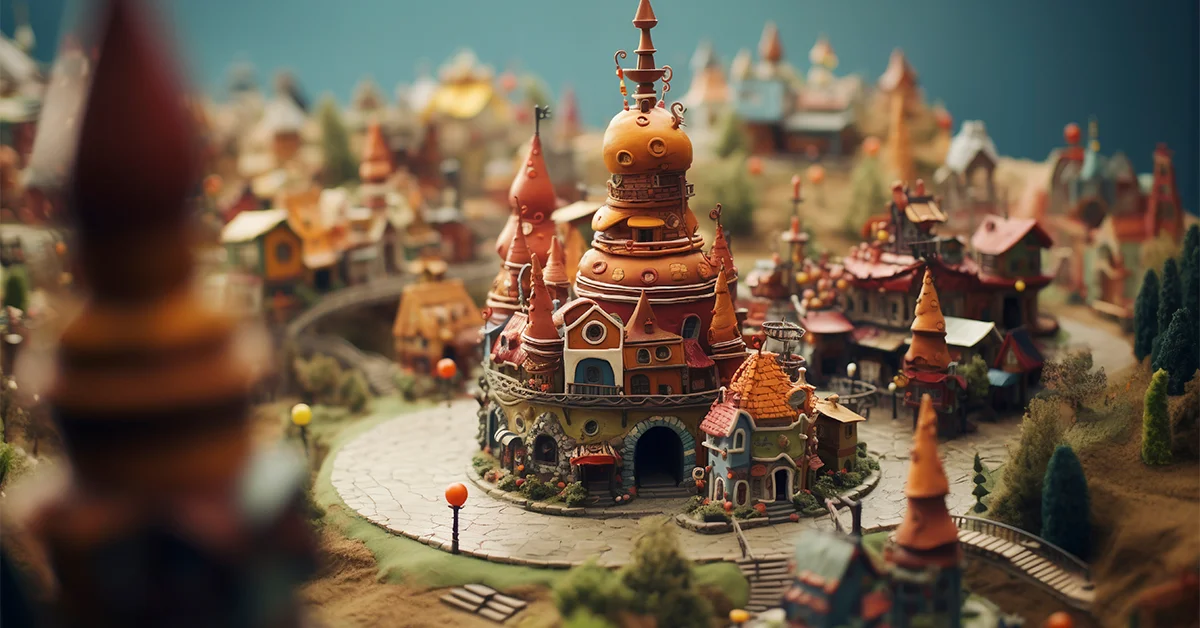

Imagine stepping into a dimly lit workshop, the air thick with resin dust, the smell of fresh primer, and the quiet hum of machines turning dreams into the tiniest works of art. That’s the world of Forgeworld. If you’ve ever held one of their resin miniatures — those high‑detail models from the Warhammer universe, the Primarchs, towering Titans, or beautifully grotesque artifacts — you know there’s magic in the making.
we’ll pull back the curtain on Forgeworld: what makes it special, how their miniatures are conceived, crafted, and refined, and why collectors and hobbyists are drawn to them despite their challenges. Whether you’re a seasoned painter, new to the hobby, or just curious about how legends in miniature are born, this journey inside the forge will give you a deeper appreciation for every detail.
TRENDING
What You Need To Know About 877-867-5139: A Quick Guide
What Is Forgeworld?
Forgeworld is a specialized division of Games Workshop, dedicated to producing highly detailed, resin‑cast models, terrain, upgrade kits, and large‑scale character miniatures. It is known for pushing the boundaries of scale, detail, and artistry in the Warhammer 40,000 and Horus Heresy lines.
Founded around 1998 under the banner of Games Workshop, Forgeworld started by making terrain and limited edition large models, then gradually expanded into full units, extra detail kits, large characters like Primarchs, and monstrous war machines called Titans.
Vision And Design: How Forgeworld’s Legends Begin
Sculpting the Idea
-
Lore & Character: Many Forgeworld miniatures, especially the Primarchs, come with rich backstories. The design process begins by asking: Who is this character? What is their personality, posture, signature weapons, history? For example, the design of Angron required capturing not only his scale but his brutal, relentless personality.
-
Scale & Proportion: Forgeworld miniatures often operate at a larger scale or character‑scale than standard infantry units. Getting the miniature to feel “right” when placed beside other minis in your army involves balancing size with detail. Too small and it loses impact; too large and it becomes unmanageable or expensive.
-
Artistic Reference & Concept Art: Once concept sketches are made, informed by lore, art history (ornament styles, armor details, weapon designs), and input from the Warhammer universe’s existing aesthetic, the sculptors may work traditionally (hand sculpting) or via digital tools. Modern workflows often rely heavily on 3D sculpting, enabling easier revisions and previews.
Prototyping & Master Sculpt
-
Master Model: The sculptor creates a master version — a high‑detail original. It might be hand sculpted in clays or resins, or digitally sculpted and printed, depending on the workflow. This stage finalizes all details including ornamentation, textures, and pose.
-
Testing & Feedback: The master model is shown to internal teams (design, lore, manufacturing) to check for consistency, visual impact, functional concerns (like ease of cleaning mold lines), and how well the miniature scales with others. Feedback may lead to adjustments in pose, armor plates, or weapon design.
From Master To Miniature: Material & Manufacture
Materials: Resin vs Plastic vs Metal
-
Resin: Forgeworld’s primary material. Resin allows very high detail, sharp edges, and crisp ornamentation like thin weapons or scrolls. However, it’s more fragile, demands more care during cleanup, is prone to warping, and is more expensive to ship.
-
Why not always plastic: Plastic injection molding for large, complex or low-volume parts (like Titans or large busts) is costly to set up. Resin casting, especially for smaller production runs or more detailed pieces, is often more feasible. Forgeworld uses resin to maintain fine detail and because many of their models are premium or collector items.
Moulding & Casting
-
The master is used to create negative molds. Silicone molds are common for resin casting. For very high-detail or large models, multiple mold pieces may be needed. Resin is poured into these molds, sometimes under vacuum or pressure to reduce air bubbles or defects. After curing, the resin casts are removed.
-
Post‑casting cleanup: Resin casting often leaves mold lines or “flash” (thin extra resin on edges), so parts must be cleaned, trimmed, and sanded. Some tiny or fine details need extra care. Resin can sometimes warp, so hobbyists or the factory may correct this with gentle heat or careful straightening.
-
Quality control: Forgeworld maintains high standards by checking parts for defects, ensuring detail, and verifying fit. Despite this, some hobbyists occasionally report variability in casting quality.
The Artist’s Touch: Painting Assembly Display
Even after the miniature arrives in your hands, the process continues. These are not plug‑and‑play models; they demand assembly, preparation, and artistic effort.
-
Preparation: Wash resin parts in warm soapy water to remove mold release agents. Inspect for thin or miscast sections. Flatten warped parts. Clean mold lines and flash. Drill small holes or pin joints if needed for assembly.
-
Assembly: Use strong adhesives like super glue designed for resin. Fit pieces carefully. Larger or heavier parts may require internal supports or pinning. If parts don’t fit perfectly, trimming or sanding can help.
-
Priming & Painting: Primer choice matters because resin can be less forgiving than plastic. Spray primers or airbrush are commonly used. Then base-coating, shading, highlighting, and weathering follow. Forgeworld miniatures reward time spent painting, with their intricate detail shining under careful brushwork.
-
Display / Gameplay Use: Some Forgeworld miniatures are display pieces; others are intended for tabletop use. Depending on their use, durability, base size, weight, and tournament legality vary. Many Forgeworld models are supported through supplements that define their gameplay roles.
What Makes Forgeworld Legendary — Unique Value & Challenges
The Unique Value
Unparalleled Detail & Character
Forgeworld offers things many standard plastic kits don’t: large characters like Primarchs, intricate ornamentation, unique allegiances, elaborate weaponry, and uncommon faction lore. This gives hobbyists pieces that feel like living pieces of the lore.
Collector Appeal
Many Forgeworld minis are limited-run, premium-priced, or collector-scale. There’s a prestige in owning them, making them not just gaming pieces but art for display or dioramas.
Expansion of Lore & Variety
Terrain kits, upgrade bits, special characters, and monstrous war machines widen the possibilities for your army or narrative, deepening the connection to the Warhammer universe.
The Challenges
Cost
Resin, premium kits, and lower volume runs all contribute to a higher price tag. Shipping and customs fees can also add up, making Forgeworld models a significant investment.
Assembly Difficulty
More parts, finer details, potential defects, and fragile components mean more work cleaning, assembling, and handling. Resin requires patience and skill.
Durability & Transport
Resin is more brittle than plastic. Thin parts can break easily. Large models are heavy and shipping them risks damage. Reinforcement or careful transport is often necessary.
Rules & Legality in Play
Not every Forgeworld model is legal in every tournament or event. Some are designated “Legends” or only usable with specific supplements. It’s important to check current rules and formats before investing in a model for gameplay.
The Recent Changes: Rebranding Merging And What It Means
In recent years, Forgeworld has been integrated more closely with Games Workshop’s core Warhammer brand. The Forgeworld website merged with the main Warhammer portal, and products have been rebranded under “Expert Kits” or similar categories.
Some miniatures previously widely available have been moved to “Legends” status, meaning fewer reprints and limited tournament support. While this has caused some concern among hobbyists, the core appeal of Forgeworld’s high-detail resin models remains strong.
Tips For Hobbyists: Getting The Best Out Of Forgeworld Miniatures
If you’re thinking of diving into Forgeworld models, here are some tips to make your experience smoother:
-
Start Small: If you’re new to resin, begin with smaller kits to learn cleaning and assembly.
-
Safety First: Resin dust is harmful—always wear a mask when sanding or trimming. Wash parts thoroughly.
-
Inspect Upon Arrival: Check for warping, missing parts, or defects right away. Report issues promptly.
-
Plan Your Paint Job: Due to intricate details, consider painting some parts before full assembly to reach hard spots.
-
Storage & Transport: Use padded cases and foam trays to protect fragile parts during transport.
-
Check Rules & Legality: Verify that the model is tournament legal if you plan to use it in organized play.
Why Forgeworld Still Inspires
Forgeworld miniatures are more than just resin and paint; they’re pieces of lore, craftsmanship, and artistry. Holding a Forgeworld Primarch or Titan feels like holding a story in your hands, shaped by skilled artists who pour personality into every rivet and scar.
For many, the time invested in building and painting these models results in immense satisfaction and pride. In a world full of mass-produced miniatures, Forgeworld stands apart, inviting hobbyists to slow down, focus, and create true legends in miniature.
Conclusion
Inside the Forgeworld is about vision, artistry, lore, craftsmanship, and passion. From first concept to final brush stroke, each miniature balances fantasy and practicality. Though challenging and costly, Forgeworld miniatures reward those who seek more than just a quick build.
If you appreciate detail, enjoy hands-on artistry, and crave unique pieces, Forgeworld represents a gold standard. Despite changes in branding and availability, its essence remains: crafting legends in miniature.
ALSO READ: Is Olive Oil A Seed Oil? Here’s What You Need To Know
FAQs
What is Forgeworld and why does it matter?
Forgeworld is a division of Games Workshop that produces highly detailed resin miniatures, terrain, and upgrade kits, mainly for Warhammer 40,000 and Horus Heresy. It matters because it offers unique, high-quality models that many plastic kits don’t, providing deeper lore and artistic value.
Are Forgeworld models tournament legal in Warhammer 40,000?
Some are, depending on the supplement or rules edition you use. Others may be designated as “Legends” and not legal in all tournaments. Always check current tournament rules.
What are the challenges of working with resin miniatures from Forgeworld?
Resin is fragile and requires careful cleaning, trimming, and assembly. Parts may warp or break easily, and the cost is generally higher than plastic models.
How do I clean and prepare a Forgeworld miniature before painting?
Wash parts in warm soapy water, remove mold lines and flash carefully, fix any warping, and assemble with suitable adhesives. Use proper safety gear to avoid resin dust exposure.
Are Forgeworld miniatures worth the investment?
If you value detail, lore, and artistry, they are. The models offer unique visual appeal and collector status, but require time, patience, and money.
General
WCO Stream: Your Go-To Spot For Nonstop Anime Action

Anime lovers, rejoice! In a world where streaming platforms are plentiful, finding a reliable, user-friendly, and vast anime source can feel like searching for a needle in a haystack. But there’s one name that’s been gaining popularity for delivering nonstop anime action — WCO Stream. If you’re looking for a place to dive deep into your favorite shows or discover hidden gems, WCO Stream’s might just be your new best friend.
In this article, we’ll explore everything you need to know about WCO Stream’s from its features and content variety to why it’s becoming a favorite among anime fans worldwide. Whether you’re a seasoned otaku or new to the anime scene, this guide will help you make the most of your streaming experience.
TRENDING
Finding The Right Plumber For Low Water Pressure Fixes
What Is WCO Stream?
Simply put, WCO Stream is an online platform that offers a vast library of anime series and movies, all available to stream for free. Unlike many other sites, WCO Stream’s focuses on providing a seamless, hassle-free viewing experience with minimal ads and a clean interface. Whether you want to binge-watch classics like Naruto and One Piece or catch up on the latest episodes of Attack on Titan or Demon Slayer, WCO Stream’s has something for everyone.
Why WCO Stream Stands Out In The Anime Streaming World
There are tons of streaming platforms out there, but what makes WCO Stream’s truly special? Here are a few standout reasons:
Extensive Anime Library
One of WCO Stream’s biggest draws is its extensive and constantly updated anime library. The platform hosts thousands of titles across various genres — action, romance, fantasy, sci-fi, horror, and more. Whether you want to watch dubbed episodes or prefer subtitles, WCO Stream’s covers both options, giving you plenty of freedom to enjoy anime the way you like.
User-Friendly Interface
Navigating through an endless list of anime can be overwhelming, but WCO Stream keeps things simple. Its clean and intuitive interface helps users quickly find what they’re looking for, whether it’s by genre, popularity, or release date. You can even search for specific titles or characters without any hassle.
Free Streaming Without Account Registration
Unlike many streaming sites that require sign-ups or subscriptions, WCO Stream allows users to watch anime for free without creating an account. This means no annoying sign-up processes or monthly fees — just click, watch, and enjoy.
Minimal Advertisements
Ads are a common complaint on free streaming sites, but WCO Stream’s manages to keep the ads to a minimum, making your viewing experience less frustrating and more immersive. Plus, they tend to be non-intrusive, so you won’t get bombarded every few minutes.
Multi-Device Compatibility
Whether you prefer watching anime on your laptop, tablet, or smartphone, WCO Stream’s works smoothly across all devices. This flexibility lets you enjoy your favorite shows anytime and anywhere.
How To Make The Most Of WCO Stream
If you’re new to WCO Stream or anime streaming in general, here are some helpful tips to enhance your experience:
Explore Genres to Find New Favorites
Anime isn’t just one thing — it’s a broad spectrum of stories and styles. Use WCO Stream’s genre filters to discover something new. Love action-packed thrillers? Check out titles under the “Action” or “Adventure” sections. Want heartwarming romance? Dive into the “Romance” category. This exploration can introduce you to series you might not find otherwise.
Check the Latest Releases Regularly
Anime fans often want to stay up-to-date with ongoing series. WCO Stream’s keeps its collection fresh by adding new episodes shortly after they air in Japan. Bookmark the “Latest Releases” section and make it part of your weekly anime routine.
Utilize the Watchlist Feature
To keep track of what you’re watching or want to watch next, use the watchlist feature. This saves time and prevents the frustration of losing your place mid-series.
Adjust Video Quality Based on Your Connection
WCO Stream offers adjustable video quality settings to suit different internet speeds. If you’re on a slower connection, lowering the quality can help prevent buffering and interruptions. On the other hand, if you have high-speed internet, enjoy HD streaming for the best viewing experience.
Engage with the Community
Many anime fans enjoy discussing episodes and theories. Although WCO Stream’s doesn’t have an official forum, you can join anime communities on social media platforms or Reddit and share your experiences about the shows you’re watching.
The Benefits Of Streaming Anime On WCO Stream
Choosing where to watch your favorite anime is an important decision, especially with so many options out there. Here’s why WCO Stream’s could be the perfect choice for you:
No Subscription Hassles
Forget about monthly fees or complicated subscription plans. WCO Stream is free to use and accessible to everyone with an internet connection.
Accessibility and Convenience
Since WCO Stream’s is web-based, you don’t need to download large files or install apps. Just open your browser, head to the site, and start watching.
Vast Collection of Both Old and New Titles
From legendary classics to the latest trending shows, WCO Stream’s has you covered. This variety ensures you’ll always find something exciting to watch.
Continuous Updates and New Content
The platform is regularly updated with new episodes and series, so you won’t miss out on your favorite anime’s newest chapters.
Things To Keep In Mind When Using WCO Stream
While WCO Stream is an excellent resource for anime fans, it’s important to remember a few points:
- Check the Legality in Your Region: Depending on your location, some content on WCO Stream’s may not be officially licensed. Always be mindful of the legal aspects of streaming in your country.
- Use Ad Blockers if Necessary: Although WCO Stream’s keeps ads minimal, you can enhance your viewing experience with a trusted ad blocker.
- Beware of Imitators: There are several sites with similar names or layouts. Always ensure you’re on the official WCO Stream’s site to avoid phishing or malware risks.
Conclusion
For anime fans looking for a reliable, user-friendly, and expansive streaming platform, WCO Stream offers a fantastic solution. It brings together a rich collection of anime titles, a smooth streaming experience, and easy accessibility — all without the need for subscriptions or sign-ups. Whether you want to catch up on the latest episodes or explore timeless classics, WCO Stream makes it simple to dive into nonstop anime action anytime you want.
Ready to immerse yourself in the world of anime? Give WCO Stream’s a try, and let the binge-watching begin!
ALSO READ: Inside The Forgeworld: Crafting Legends In Miniature
FAQs
What is WCO Stream?
WCO Stream is a free online streaming platform offering a vast collection of anime series and movies. It allows users to watch anime without registration or subscription, providing both dubbed and subtitled options.
Is WCO Stream free to use?
Yes, WCO Stream’s is completely free to use. You can watch unlimited anime content without paying or signing up.
Can I watch WCO Stream on my mobile device?
Absolutely! WCO Stream is compatible with laptops, tablets, and smartphones, so you can enjoy anime on the go.
Does WCO Stream have the latest anime episodes?
Yes, WCO Stream regularly updates its library with new episodes shortly after they air, helping fans stay current with their favorite shows.
Is WCO Stream legal and safe to use?
WCO Stream offers free streaming but may not have official licenses for all content in every region. Always check local laws regarding online streaming. For safety, ensure you access the official website and consider using ad blockers to avoid intrusive ads.
General
Riding Raw: Why The Yamaha FZ09 Still Turns Heads

Walk down any city block or glance at a group ride meet-up, and there’s always that one bike that grabs your attention—not because it’s the loudest, or the most expensive, but because it has presence. The Yamaha FZ09 is one of those bikes. It’s not just the aggressive lines, the raw triple-cylinder growl, or the minimalist styling—it’s the energy it gives off. Even years after its release, the FZ09 continues to turn heads. But why?
Let’s dive into what makes the Yamaha FZ09 such an icon, why it still feels relevant in today’s crowded motorcycle market, and why it’s a favorite among both new and experienced riders.
TRENDING
Certo Detox: Does This Viral Cleanse Really Work?
What Is The Yamaha FZ09?
The Yamaha FZ09 (also known as the MT-09 in many parts of the world) is a naked sportbike that debuted in 2014. It marked a bold shift in Yamaha’s lineup, delivering an affordable, aggressive, and fun-to-ride motorcycle powered by an 847cc inline-three engine. It was designed to fill a void between smaller 600cc bikes and larger liter-class monsters, offering a lightweight chassis and massive torque in a daily-ridable package.
But the FZ09 isn’t just about numbers—it’s about raw riding pleasure. It delivers unfiltered performance in a way that feels both thrilling and controllable.
That Triple-Cylinder Magic
The beating heart of the FZ09 is its unique three-cylinder engine. It’s what sets the bike apart from nearly everything else on the market.
Where a four-cylinder engine might offer silky smooth power and a twin might provide thumping torque, the triple strikes a perfect balance. It revs fast, pulls hard from low RPMs, and sounds absolutely glorious. There’s a raw edge to it—like a streetfighter that’s just barely domesticated.
The power delivery is linear but exciting. Twist the throttle, and the bike leaps forward with urgency, especially in the midrange. Whether you’re riding through tight city streets or powering out of a corner on a country road, the engine makes every ride feel alive.
Aggressive Head-Turning Styling
The FZ09 looks as mean as it rides. From its angular headlight to its sculpted tank and exposed frame, this bike carries the kind of design that refuses to blend in.
It’s not over-styled or cluttered. It’s stripped down, purposeful, and confident. The wide handlebars, short tail, and aggressive stance give it a muscular look—like it’s ready to pounce.
Even newer riders who don’t know much about motorcycles are often drawn to the FZ09 because of its streetfighter appeal. It’s the kind of machine that makes you look twice when it pulls up next to you at a red light.
Lightweight And Nimble
The FZ09 weighs in at just over 400 pounds wet, which is impressively light for a bike with this much power. The result? Agility.
In traffic, it zips through gaps with ease. On twisty roads, it flicks from corner to corner with minimal effort. It feels playful, almost like a supermoto at times—except with way more horsepower.
This lightness is a big reason why the FZ09 is so engaging to ride. It doesn’t feel like it’s doing the work for you—you’re part of the experience. It rewards skilled input, but doesn’t punish you for having fun.
A True Street Weapon
While many bikes are built for track days or long-haul touring, the FZ09 is unapologetically a street bike. It thrives in real-world conditions—stop-and-go traffic, quick lane changes, and city potholes.
The upright riding position keeps you comfortable, while the wide bars give you leverage for fast directional changes. It’s one of those bikes you can hop on, ride for 30 minutes or 3 hours, and always get off with a smile.
This street-focused nature is why so many riders refer to it as a “do-it-all” bike. Commuting, weekend blasts, even light touring—it can handle all of it, while still looking aggressive and sounding incredible.
Minimal Electronics, Maximum Fun
When it first launched, the FZ09 was refreshingly simple. No ride-by-wire, no cornering ABS, no rain mode—just a twist-and-go thrill machine. Later models added features like traction control, ride modes, and even a quick shifter, but the core riding experience has always remained raw and authentic.
There’s something rewarding about that simplicity. You’re not being held back by a dozen computer systems. It’s just you and the bike, with nothing getting in the way.
That said, Yamaha has struck a good balance in newer models. The electronics now add to the ride rather than take away from it. You can dial in the power delivery, soften the throttle response, and adjust traction settings—all while keeping that visceral connection alive.
Massive Modding Potential
Another reason the FZ09 turns heads? Customization.
This bike has one of the most active and passionate modding communities out there. From custom exhausts and tail tidies to LED kits and bar-end mirrors, riders love making their FZ09s one of a kind.
Just a few tasteful mods—an aftermarket exhaust, a tidy tail kit, or a new set of levers—can completely change the look and feel of the bike. And with so many affordable parts available, personalizing your FZ09 doesn’t require a huge investment.
It’s common to see unique builds on the road, with riders proudly showing off their take on the naked bike platform.
Still Competitive In 2025
You might wonder: with newer bikes coming out every year, how does the FZ09 hold up?
The answer? Exceptionally well.
Even over a decade after its debut, the FZ09 (and its updated MT-09 siblings) continues to outperform its price point. Newer models have refined suspension, updated styling, better electronics, and improved comfort—but the soul of the bike remains untouched.
It still offers more excitement than many bikes in its class, and often for less money. And that means people still notice it. The head-turning factor hasn’t faded—it’s only evolved.
The FZ09 Experience Is Addictive
There’s a certain feeling you get when you ride the FZ09 that’s hard to describe until you’ve experienced it. The engine pulses beneath you, the throttle begs to be twisted, and the exhaust roars out behind you like a war cry.
You feel connected to the road. You feel powerful. And most of all, you feel alive.
This connection is why so many riders who try the FZ09 fall in love with it. It’s not just a bike—it’s an experience. And that’s something you can’t help but notice when it rides by.
Who Is The Yamaha FZ09 For?
The beauty of the FZ09 is its versatility. It appeals to:
Intermediate riders looking to upgrade from a beginner bike
Experienced riders who want something lighter and more fun for everyday riding
Modders who want a solid base for a custom project
Weekend warriors who crave an exciting, visceral ride
It’s not ideal for long-distance touring or two-up comfort, but for solo riders who want a raw, connected, powerful street machine, the FZ09 is hard to beat.
Common Upgrades That Enhance The Experience
Want to turn even more heads? These are some of the most popular and effective FZ09 mods:
Exhaust System – Deeper sound and more personality
Tail Tidy – Cleans up the rear end for a sportier look
Bar-End Mirrors – Sleek, modern styling upgrade
LED Turn Signals – Bright, eye-catching, and stylish
Suspension Upgrades – Improves handling for aggressive riding
Seat Upgrades – Adds comfort for longer rides
Quickshifter – More seamless gear changes
Each of these adds performance, personality, or visual appeal—helping your FZ09 stand out even more.
Conclusion
The Yamaha FZ09 isn’t just a motorcycle—it’s a statement. A statement that says you value raw power, minimalist design, and the thrill of the ride.
Even with all the new models, trends, and technologies that have emerged in the motorcycle world, the FZ09 continues to captivate riders and bystanders alike. It turns heads not because it’s trying to, but because it can’t help it.
It’s a modern classic. A motorcycle that still feels rebellious, bold, and alive.
So if you’re riding one, keep the throttle twisted and the revs high—you’re part of a legacy that refuses to fade.
ALSO READ: Stiffy Drive: The Retro Tech That Refuses To Quit
FAQs
What is the Yamaha FZ09?
The Yamaha FZ09 is a naked sportbike known for its 847cc triple-cylinder engine, lightweight chassis, and aggressive streetfighter styling. It’s designed for real-world riding and delivers a raw, engaging experience.
Is the Yamaha FZ09 beginner-friendly?
It’s powerful and responsive, so it’s better suited for intermediate riders. However, confident beginners with restraint and respect for the throttle can manage it with proper guidance.
How reliable is the FZ09 for daily riding?
Very reliable. With regular maintenance and care, the FZ09 can serve as a dependable daily rider. Many owners use it for commuting and weekend rides alike.
Can the FZ09 be used for long-distance touring?
While not built for touring, it can handle longer rides with comfort upgrades like a better seat, small windscreen, and soft luggage.
Why do people still buy the FZ09 in 2025?
Because it still delivers unmatched fun, a unique engine character, standout looks, and great value. It remains one of the most exciting bikes in its class, even years after its debut.
-

 Entertainment9 months ago
Entertainment9 months agoExplore The Kristen Archives: A Treasure Trove Of Stories & More
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoWhat is O Farming: How to Make Money Online and Its Start-Up Benefits
-

 Law9 months ago
Law9 months agoProtect Your Vehicle with These Smart Motor Insurance Strategies
-

 Entertainment2 years ago
Entertainment2 years agoSandra Orlow: Exploring the Life and Legacy of a Cultural Icon
-
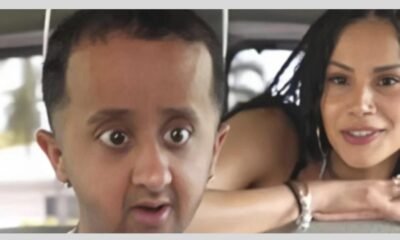
 General2 years ago
General2 years agoBaby Alien Fan Bus: Watch Parts 2 & 3 on Twitter, Reddit!
-

 Technology2 years ago
Technology2 years agoGeekzilla Radio: Your Portal to the Ultimate Geeky Adventure!
-

 General2 years ago
General2 years agoDiana Nyad & Bart Springtime: A Swim to Success
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoTex9.Net Crypto: Fast, Secure International Money Transfers with Competitive Rates
