Pets
Discover The Finnish Raccoon: A Unique Wildlife Experience

Finland is known for its stunning natural landscapes, ranging from dense forests to pristine lakes, and its abundance of wildlife. Among the more interesting creatures that inhabit the Finnish wilderness is the Finnish raccoon, a relatively new addition to the country’s diverse fauna. While raccoons are native to North America, their introduction to Finland has sparked curiosity and concern alike. In this article, we will explore the Finnish raccoon’s origin, its impact on local ecosystems, and the unique experiences that come with observing this fascinating animal in its adopted homeland.
TRENDING
Hawthorn M Class HMS Mentor: History And Significance
The Introduction Of The Raccoon To Finland
Origins of the Finnish Raccoon
Raccoons (scientific name Procyon lotor) are native to North America, where they are well known for their distinctive appearance and resourceful behavior. However, the introduction of raccoons to Europe began in the early 20th century, with Finland being one of the more recent countries to see the species establish itself.
The first confirmed sighting of a raccoon in Finland occurred in the 1990s, when a few individuals were spotted in the wild. These raccoons are believed to have arrived either through illegal releases or accidental escapes from captivity. Despite their foreign origins, raccoons quickly adapted to Finland’s environment, finding favorable conditions in the country’s dense forests and moderate climate.
Today, raccoons are no longer considered rare in Finland, and their population has been steadily growing. They can now be found in various parts of the country, particularly in the southern and central regions.
How the Raccoon Thrives in Finland
The Finnish climate is quite different from the raccoon’s native habitat in North America. However, the adaptable nature of the raccoon has allowed it to thrive in Finland. Raccoons are omnivorous and opportunistic feeders, which means they can adjust to a wide range of food sources. In Finland, they often forage for fruits, berries, small mammals, birds, and even human food waste. Their ability to live off a variety of resources has enabled them to survive and even flourish in areas where other species might struggle.
Furthermore, the Finnish landscape, with its vast forests, wetlands, and river systems, offers an ideal environment for raccoons to establish their dens. These animals prefer locations near water, where they can forage for food and create secure homes in hollow trees or burrows. Finland’s abundant lakes and rivers provide a perfect setting for the raccoon to live comfortably.
The Raccoon’s Impact On The Finnish Ecosystem
Ecological Disruption
The introduction of non-native species can often have unintended consequences for the local ecosystem, and the raccoon is no exception. In Finland, the raccoon has caused concern among wildlife experts due to its potential to disrupt the natural balance. As an omnivorous scavenger, the raccoon competes with native species for food sources. For example, it may outcompete native birds for nesting sites or consume the eggs of vulnerable species. Additionally, raccoons are known to prey on small mammals and insects, which could affect the populations of local fauna.
One of the most notable impacts of the Finnish raccoon is on native plant life. Raccoons have been observed digging up and disturbing the soil in search of food, which could potentially damage plant roots and lead to erosion in certain areas. As opportunistic feeders, raccoons may also spread invasive plant species by unintentionally transporting seeds in their fur or waste.
Disease and Public Health Concerns
Raccoons are also known carriers of diseases that could be harmful to other wildlife, domestic animals, and even humans. In North America, raccoons are infamous for being carriers of rabies, a viral disease that can be transmitted through bites or saliva. Although rabies is not currently a major concern in Finland, the presence of raccoons increases the risk of introducing this deadly disease to the local animal population.
In addition to rabies, raccoons are potential hosts for parasites like ticks, roundworms, and leptospirosis, which could further disrupt the health of Finland’s wildlife. For instance, the raccoon roundworm (Baylisascaris procyonis) can pose serious risks to other animals and even humans if proper precautions are not taken when interacting with raccoon habitats.
Efforts to Control the Raccoon Population
Given the raccoon’s ecological impact, Finland has implemented measures to control their population. These efforts include trapping and monitoring the spread of raccoons across the country. Authorities work with wildlife experts to track raccoon sightings, gather data, and ensure that their growth remains in check. However, since the raccoons are already established in various parts of the country, it is unlikely that they will be fully eradicated anytime soon.
Unique Wildlife Experiences With The Finnish Raccoon
Where to Spot Raccoons in Finland
Although they are primarily nocturnal animals, raccoons can sometimes be spotted during the day, particularly in areas near water or human habitation. The best places to see Finnish raccoons are in the southern regions of the country, where the population is densest. The cities of Helsinki, Turku, and Tampere are known hotspots for raccoon sightings, especially in suburban neighborhoods with large green spaces.
However, raccoons can also be found in rural areas, forests, and around lake districts. They often live in proximity to urban centers, where they scavenge for food in trash bins or gardens. Visiting Finland’s nature reserves or taking guided tours that focus on wildlife observation can increase your chances of spotting a raccoon in its natural habitat.
Ecotourism and Raccoon Watching
In recent years, raccoon watching has become an emerging form of ecotourism in Finland. Nature enthusiasts and photographers have begun to take an interest in observing raccoons, particularly in areas like the Archipelago Sea or the southern coast. Some tour operators offer special nocturnal wildlife tours, where visitors can learn about raccoons’ behavior and ecology while observing them in the wild.
These tours not only provide a unique chance to see raccoons but also educate the public about the importance of managing the population and protecting Finland’s native wildlife. For many tourists, encountering a Finnish raccoon in its natural habitat is a memorable experience that adds a new dimension to their appreciation of Finland’s diverse ecosystems.
Raccoons in Finnish Folklore
The raccoon’s arrival in Finland has sparked interest in its role within Finnish folklore. While raccoons are not traditionally part of Finnish mythology, their distinctive appearance and behavior have inspired local stories and legends. Finnish wildlife experts often draw parallels between the raccoon’s cleverness and resourcefulness and traditional stories of mythical tricksters.
Some local folklore suggests that raccoons, like the fox or the raven, are symbols of cleverness and adaptability. As Finland’s human population continues to learn about the raccoon’s behaviors, it is possible that the animal will become more deeply integrated into modern Finnish cultural stories.
Conclusion
The Finnish raccoon is a fascinating species that has made its mark on the Finnish landscape, despite its non-native origins. While the raccoon has successfully adapted to Finland’s environment, its presence also raises important questions about the management of invasive species and their impact on local ecosystems. Whether you are a wildlife enthusiast or an ecotourist, the Finnish raccoon offers a unique opportunity to witness the adaptability and resilience of one of North America’s most iconic creatures in a new and unexpected environment. With continued research and management efforts, Finland can find a way to balance the raccoon’s presence with the preservation of its rich natural heritage.
ALSO READ: Mike Lindell Net Worth 2024: The Rise Of The MyPillow Mogul
FAQs
What is a Finnish raccoon?
A Finnish raccoon is a non-native species of raccoon (Procyon lotor) that has established itself in Finland, primarily in the southern and central regions. Originally from North America, the raccoon was introduced to Europe and eventually spread to Finland, where it has adapted to local environments.
Are raccoons native to Finland?
No, raccoons are not native to Finland. They were introduced to Europe from North America in the early 20th century, and the first confirmed sightings of raccoons in Finland occurred in the 1990s.
What impact do raccoons have on the Finnish ecosystem?
Raccoons can disrupt Finland’s ecosystem by competing with native species for food, damaging plant life, and spreading diseases. They may also prey on small mammals, birds, and eggs, affecting local wildlife populations.
Can I see raccoons in the wild in Finland?
Yes, raccoons can be spotted in the wild, particularly in southern Finland and urban areas near forests or lakes. There are also guided wildlife tours that allow visitors to observe raccoons in their natural habitat.
Are raccoons dangerous to humans in Finland?
While raccoons in Finland are generally not aggressive toward humans, they can carry diseases such as rabies, parasites, and leptospirosis. It is important to avoid direct contact with raccoons and to take proper precautions when in areas where they are present.
Pets
How to Choose One of the Best Dog Harnesses in USA for Your Pet’s Safety and Comfort
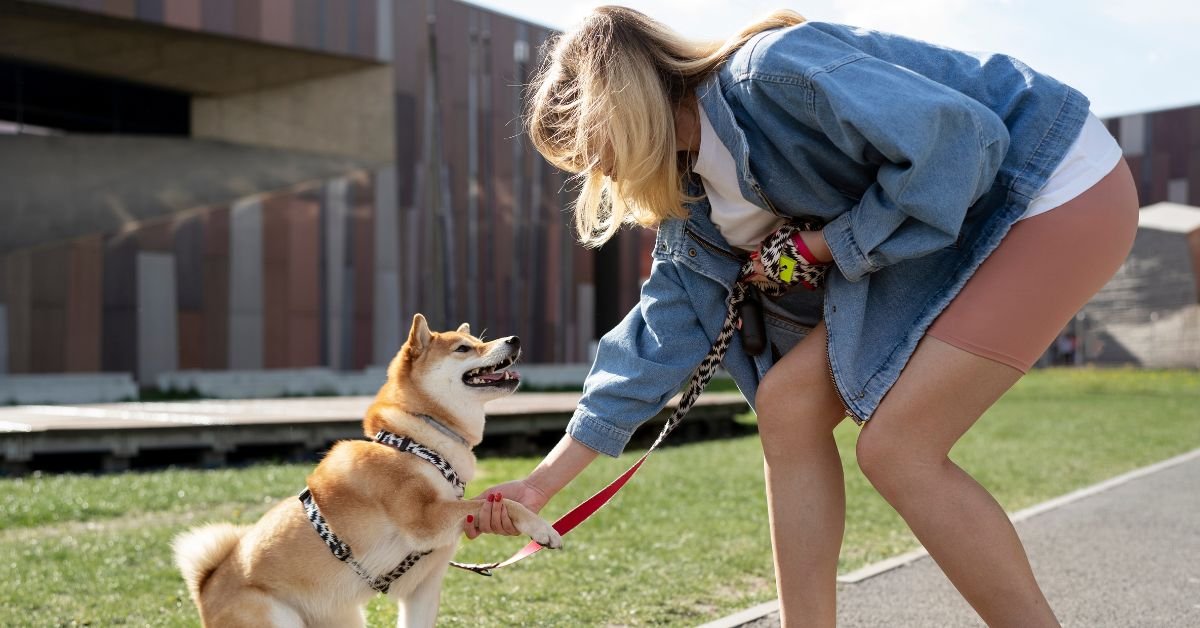

Selecting appropriate canine restraint equipment requires careful consideration of biomechanical factors, material durability, and breed-specific anatomical requirements. Modern pet owners increasingly recognize that traditional collar-based restraint systems can cause tracheal damage, cervical spine compression, and behavioral stress responses in dogs. Research conducted by veterinary orthopedic specialists indicates that one of the best dog harnesses in USA demonstrates superior force distribution across the chest and shoulders, reducing concentrated pressure points that commonly occur with collar systems. This comprehensive analysis examines the technical specifications, safety protocols, and performance metrics essential for making informed harness selection decisions.
Understanding Biomechanical Force Distribution
The physics of canine locomotion reveals why harness design significantly impacts pet comfort and safety. When dogs pull against traditional collars, forces concentrate directly on the trachea and cervical vertebrae, creating pressure readings that can exceed 40 pounds per square inch in medium-sized breeds. Harness systems redistribute these forces across broader surface areas, typically reducing peak pressure by 60-75% according to veterinary biomechanics studies.
Front-clip harnesses introduce additional complexity by redirecting pulling forces laterally, which can affect natural gait patterns. Research from canine rehabilitation centers suggests that while front-clip designs effectively reduce pulling behavior, they may create compensatory movement patterns in the shoulders and hindquarters during extended use.
Material Science and Durability Considerations
Modern harness construction utilizes advanced textile engineering principles to balance strength, flexibility, and comfort. Nylon webbing remains the gold standard for load-bearing components, with tensile strength ratings typically ranging from 500 to 1,200 pounds for quality harnesses. However, the weave density and thread count significantly influence both durability and comfort against the dog’s skin.
Padding materials have evolved beyond simple foam inserts to include memory foam composites, gel-infused polymers, and moisture-wicking synthetic fabrics. These advanced materials address common issues like pressure sores, heat retention, and bacterial growth that plagued earlier harness designs.
Breed-Specific Anatomical Adaptations
Different dog breeds present unique anatomical challenges that affect harness fit and function. Brachycephalic breeds like Bulldogs and Pugs require harness designs that accommodate shortened airways and modified chest proportions. Deep-chested breeds such as Greyhounds and Great Danes need harnesses with extended chest panels to prevent interference with natural breathing mechanics.
Working breeds often require reinforced stress points and additional adjustment mechanisms to accommodate seasonal weight fluctuations and muscle development changes. Sporting breeds benefit from harnesses designed with range-of-motion considerations for activities like agility training and field work.
Measurement Protocols and Fit Optimization
Proper harness sizing requires multiple anatomical measurements beyond simple chest circumference. Professional fit protocols include girth measurements at the widest chest point, neck-to-chest length, and shoulder blade positioning assessments. Seasonal adjustments become necessary as coat thickness changes and muscle mass fluctuates with activity levels.
Temperature regulation considerations also influence harness selection, particularly for breeds with dense undercoats or those living in extreme climates. Ventilation channels, moisture-wicking materials, and reflective elements contribute to thermal management during extended wear periods.
CLIC
Pets
Integrating Pet Training into Company Wellness Programs

Work can get busy and stressful, so it is important to find fun ways to help employees feel better. One creative idea is adding dog training to company wellness programs. Imagine coworkers laughing and learning together while they teach dogs new tricks. It’s not just fun- it helps people relax, connect, and work better as a team. And let’s face it, spending time with dogs can make anyone’s day better.
Let’s explore how this simple idea can make a big difference at work.
The Benefits of Incorporating Pet Training
More and more companies are seeing the benefits of full-body and mind wellness programs. Adding pet training to these activities can help create a healthier, more positive workplace.
When employees spend time with animals, it lifts their mood and helps them feel more connected. This kind of experience supports emotional balance and makes it easier for people to handle stress.
Team Building Through Training
Pet training can also be a great way to build stronger teams. During training sessions, employees have to work together, which helps them communicate more effectively.
Teaching a dog takes patience, teamwork, and understanding- skills that are useful on the job, too. Regular practice can create a friendlier and more supportive work environment while helping people build important social skills.
Cost-Effectiveness of Integrating Pet Training
Starting a pet training program can be less expensive than some other wellness programs, like gym memberships or therapy services. Companies can work with local pet trainers, such as OverWatch K9 Academy, to create fun and useful workshops.
These sessions can be designed to fit the company’s needs and keep employees interested. Over time, this kind of program can bring lasting benefits, making it a smart choice for wellness budgets.
Reducing Stress through Hands-On Activities
Employees deal with all kinds of stress at work, like deadlines and tough projects. Doing something active, like dog training, gives them a chance to take a break and relax in a calming space.
Working with a dog can bring joy and a sense of play, helping people feel better and handle tough days more easily. It also gives them a healthy way to let out emotions and feel more balanced.
Implementing a Pet Training Program
Starting a pet training program at work can be pretty easy. First, ask employees if they’re interested and if they have any experience with pets.
Then, set up workshops for different skill levels. Having regular sessions led by skilled trainers helps make sure everyone learns while having fun.
Creating a friendly space where employees can share tips and stories also makes the experience better. Letting them bring their pets to work during these sessions adds to the fun and can turn training into a favorite workplace tradition.
A Win-Win for Employers and Employees
Integrating pet training into corporate wellness programs is not just a trend; it is a transformative approach that can dramatically enhance employee well-being and workplace culture. When employees feel happier and less stressed, productivity naturally improves. Consider partnering with platforms to bring a unique and valuable training experience to your organization. By doing so, you can foster an environment of collaboration, increased morale, and enhanced mental health.
Pets
Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Best Treats for Your Beloved Pet

Every pet owner wants to see their beloved pet happy and healthy. One of the simplest ways to bring a smile to their face is through delicious and nutritious pet treats. But with so many options available, picking the right ones can be overwhelming.
This ultimate guide will help you wade through the choices and ensure you’re making the best decisions for your beloved companion. Keep on reading to learn more.
Understanding Your Pet’s Needs
Just like humans, pets have unique dietary requirements. Understanding these needs is crucial when selecting healthy pet treats. Here are some factors to consider:
- Age
- Weight
- Health Conditions
- Type
Types of Pet Treats
In the vast market for pet snacks, there are a few main categories. Each type has its pros and cons:
Dog Treats
Dog treats come in many types like biscuits, jerky, and chewy sticks. Pick ones made with good ingredients and not too many calories. Some help clean teeth too.
Cat Treats
Cats like treats that are crunchy or meaty. Choose treats with healthy stuff like vitamins and protein. Good treats help keep your cat strong.
Training Treats
Training treats are small and soft. They help pets learn by giving quick rewards. Use ones that are low in calories so your pet stays healthy.
Ingredients Matter
When browsing for pet treats, always read the label. High-quality treats are typically made with real meat, whole grains, and vegetables. Be wary of treats containing fillers like corn or soy. Opt for:
- Natural ingredients
- No artificial preservatives
- Animal protein sources, like chicken or fish
- Added vitamins and minerals
Homemade Treats: A Personal Touch
If you enjoy spending time in the kitchen, consider making homemade pet treats. This allows you to control every ingredient. Some easy recipes involve simple components like peanut butter, pumpkin, and oats. Just make sure any ingredients you use are safe for your pet.
Store-Bought Treasures
Purchasing dog treats and cat treats from stores can be convenient. Look for reputable brands that prioritize quality. Check for customer reviews and consider a brand’s reputation before purchasing. Local pet stores often have knowledgeable staff who can recommend the best options.
Rewarding with Purpose
Using treats is about more than just enjoyment; it’s bonding time and training reinforcement. Effective use of treats can:
- Strengthen your companionship
- Encourage good behavior
- Assist in training new commands
Remember to use them wisely! Moderation is key, so avoid overloading your pet with snacks.
Choosing the Right Treats
In the end, selecting the right treats boils down to understanding your pet’s individual preferences and needs. Make sure to balance their health and enjoyment by taking the time to choose wisely. By focusing on quality ingredients and considering your pet’s specific requirements, you’ll be well on your way to making treat time a truly delightful experience.
Make Treat Time Special for Your Beloved Pet
At the end of the day, knowing your beloved pet is getting the best of the best in snacks makes all the difference. Whether you opt for store-bought solutions or craft delightful homemade tasty bites, the joy it brings your beloved best friend is priceless. Treat them with love and care!
-

 Entertainment8 months ago
Entertainment8 months agoExplore The Kristen Archives: A Treasure Trove Of Stories & More
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoWhat is O Farming: How to Make Money Online and Its Start-Up Benefits
-

 Law9 months ago
Law9 months agoProtect Your Vehicle with These Smart Motor Insurance Strategies
-

 Entertainment2 years ago
Entertainment2 years agoSandra Orlow: Exploring the Life and Legacy of a Cultural Icon
-
 General1 year ago
General1 year agoBaby Alien Fan Bus: Watch Parts 2 & 3 on Twitter, Reddit!
-

 Technology2 years ago
Technology2 years agoGeekzilla Radio: Your Portal to the Ultimate Geeky Adventure!
-

 General1 year ago
General1 year agoDiana Nyad & Bart Springtime: A Swim to Success
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoTex9.Net Crypto: Fast, Secure International Money Transfers with Competitive Rates
